Deir el-Medina
De Wikipedia, la enciclopedia libre
Contenido
Deir el-Medina, poblado egipcio fundado por Tutmosis I, faraón de la dinastía XVIII. Situación:
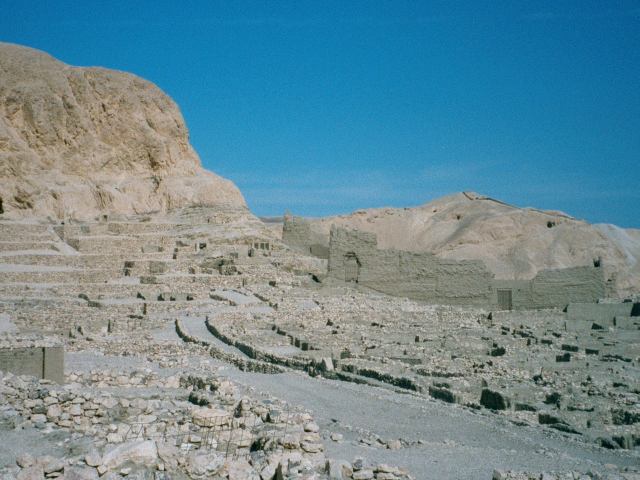
A la entrada del Valle de las Reinas y cerca del de los Reyes, se encuentran los restos del que fuera el más próspero poblado de obreros y artesanos del Antiguo Egipto: Set Maat "El lugar de la Verdad" (nombre egipcio), Deir el-Medina (nombre árabe), localidad situada en un pequeño valle en la región tebana, próximo a la colina de Qurnet Mura, en la ribera occidental del Nilo, frente a Tebas, actual Luxor (Egipto)
Durante mucho tiempo sufrió saqueos debido al expolio de antigüedades, ya que era un sitio muy conocido por la abundancia, belleza y riqueza de los objetos que se encontraban en sus cercanías. Sin embargo aún se conservan muchas evidencias arqueológicas: tumbas, casas, ajuares, que hacen de este lugar el poblado del Antiguo Egipto mejor conocido.
Contenido |
Historia [editar]
Al comienzo del Imperio Nuevo, Tutmosis I, decide abandonar la construcción de mastabas y pirámides debido a los saqueos a que eran sometidas, y ordena comenzar su tumba en un lugar más protegido, excavando la ladera de la montaña, fundando Set Maat (Deir el-Medina) como lugar de residencia para los obreros y artesanos ocupados en la construcción. Sus sucesores construyeron sus tumbas en el mismo lugar durante unos 500 años, tiempo durante el cual el poblado estuvo habitado.
Se fundó con dimensiones reducidas: cuarenta casas rodeadas por una muralla, pero nunca dejó de crecer, alcanzando su máximo esplendor en tiempos de Seti I y Ramsés II, con cincuenta casas en el interior del recinto amurallado y setenta fuera de él. Fue abandonado en tiempos de Esmendes I, alrededor del 1170 a. C. Un segundo renacimiento se produjo con la Dinastía Ptolemaica, pero no llegó a la prosperidad anterior y pronto fue de nuevo abandonado.
El poblado [editar]
El pueblo se llamaba simplemente Pa Demi, el poblado.[1] La muralla delimitaba un área rectangular dentro de la cuál se distribuían las viviendas a lo largo de una calle que comenzaba en la puerta del recinto y atravesaba todo el pueblo. El muro posterior de cada edificio estaba adosado a la muralla.
Eran casas de una sola planta, con pavimento de piedra y paredes de adobe,[2] materiales que compartían con el resto de los edificios, excluidos los templos y tumbas. Se techaban con troncos cubiertos de hojas de palmera y barro y quedaban separadas entre sí por un muro.
De planta rectangular, tenían cuatro pequeñas salas, una tras otra: la primera era un vestíbulo con un altar, y la última parece ser la cocina, ya que en ella se han encontrado restos de ceniza. De allí partía una escalera para subir a la terraza.
El mobiliario y demás objetos cotidianos, como espejos, juegos de mesa, se conocen gracias a la tumba del arquitecto Kha y su esposa Merit, que nos ha llegado intacta con un rico ajuar, aunque probablemente el de los trabajadores fuese más modesto.
Ciudadanos [editar]
Conocemos los detalles de su vida cotidiana gracias a los ostracas, trozos de cerámica, o piedra caliza, usados como soporte para sus anotaciones, al ser el papiro muy caro, que se han encontrado en el basurero de la ciudad.
Los obreros formaban parte de la base social, junto con los campesinos, pero entre ellos existían diferencias notables dependiendo de que fueran artesanos, obreros comunes o desempeñasen alguna labor administrativa: escribas, médicos, etc., además de toda la gente necesaria para el funcionamiento de la ciudad: todas aquellas labores necesarias para el autoabastecimiento, incluidas las agrícolas. El Estado deseaba pocos contactos con el exterior, para mantener toda la discreción posible sobre la construcción de las tumbas, por lo que suministraba todo lo necesario, inclusive el transporte de agua desde el río, al estar el pueblo situado en una zona desértica.
Trabajo [editar]
Antes de dar comienzo a cualquier obra, artesanos y obreros firmaban un contrato en el que se ajustaba la duración del trabajo y el salario. Este se pagaba en especie, en forma de raciones mayores o menores en función de la categoría de cada cual. Además, las familias cultivaban pequeñas parcelas y criaban cerdos, cabras y ovejas.
El periodo laboral era de diez días, a razón de ocho horas diarias, y comenzaba al salir el sol. Al acabar, no regresaban al pueblo sino que pasaban la noche en unas casas provisionales, levantadas al lado del Valle de los Reyes.
Sólo se podía faltar por enfermedad, por el cumpleaños de la madre o por ausencia de la mujer, pero en la práctica había toda clase de excusas: cuidar un burro enfermo, preparar una fiesta, o la muerte de un familiar, motivos todos ellos que, en teoría, conllevaban una sanción.
Escribas [editar]
Seguían de cerca los trabajos y registraban cualquier acontecimiento, el progreso diario de la obra, el material utilizado, las ausencias al trabajo, etc. Este trabajo se llamaba "El diario de la Tumba", y lo realizaba el "Escriba de la Tumba" que era el representante del estado en el poblado. Todos los aspectos burocráticos eran manejados por él.
Médicos [editar]
Tenían la obligación principal de mantener en forma a los obreros, aunque también atendían al resto de la población. Era una tarea realizada por la "Mujer Sabia" que se creía tenía poderes sobrenaturales y amplios conocimientos (para la época) de medicina.
Obreros [editar]
Eran los encargados de excavar las tumbas en la ladera de la montaña. Trabajaban en cuadrillas divididas en dos grupos, al frente de cada uno de ellos había un capataz y un ayudante. Dado que algunas galerías alcanzaban los cien metros, se utilizaba iluminación artificial a base de lámparas de aceite suministradas por el almacén real de la zona.
Los albañiles daban forma a las diferentes estancias, ocultando cuidadosamente el acceso, para evitar en lo posible el saqueo de la tumba, que ya era una práctica habitual.
Artesanos [editar]
Entraban en acción cuando las cámaras estaban listas, siendo responsables de la decoración. Debían pintar las paredes, la mayoría de las veces con las instrucciones del Libro de los Muertos, hacer las estatuillas que representaban al rey y a sus criados, ushebti, y confecionarle todo el ajuar, para utilizarlo en la otra vida, por supuesto, ricamente decorado.
Ocio [editar]
Cada diez jornadas volvían a sus casas, dedicando el día libre a construir sus propias tumbas, en las que nos han dejado hermosas pinturas, visitar lugares de culto cercanos o realizar trabajos por cuenta ajena para redondear ingresos.
Casi todos los trabajadores estaban organizados en cofradías, y aprovechaban los días libres para reunirse.
Justicia [editar]
Las faltas penales las sancionaba el chaty, las laborales los capataces, pero sobre las demás cuestiones dictaminaba un tribunal compuesto por los propios obreros, siendo el castigo más aplicado el apaleamiento público.
La primera huelga de la historia [editar]
En tiempos de Ramsés III, hacia 1170 a. C., el pago de salarios se retrasó más de lo acostumbrado, y los trabajadores, empujados por el hambre, abandonaron sus trabajos y se lanzaron a las calles hasta conseguir sus objetivos.
Años después, con Ramsés IX y Ramsés X se repitió la historia.
Resumen [editar]
Fue un pueblo ocupado por trabajadores bien alimentados que llevaban una vida relativamente acomodada, y que sólo pagaban el impuesto personal, pero no los diezmos.
Deir el-Medina tuvo su mejor época con Ramsés II: con la decadencia que comenzó con la Dinastía XX, la desorganización llegó también allí, hasta el abandono total con la Dinastía XXI, que trasladó la capital a Tanis en el Delta y abandonó la necrópolis tebana: Deir el-Medina ya no tenía razón de ser.
Restos arqueológicos en la zona [editar]
- El poblado de los artesanos
- El Valle de los Reyes
- El Valle de las Reinas
- Un templo ptolemáico
- La necrópolis: con las tumbas de Senedyem, Inerjau, Kha (única intacta) y Pashedu.
Véase también [editar]
Referencias [editar]
Citas [editar]
- ↑ Egipto.com. «Pa Demi». Valle de los artesanos. Consultado el 08, 10 de 2008.
- ↑ Los ladrillos de adobe se fabricaban con lodo del Nilo, arena y paja. Se les daba forma con un molde rectangular de madera y se dejaban secar al sol.
Fuentes [editar]
- Montet, Pierre (1990). La vida cotidiana en Egipto en tiempos de los Ramsés. Madrid: Temas de Hoy. ISBN 9684060165.
- Hernández, David (1998) «El poblado de los constructores de tumbas» Muy especial. n.º 33, pág. 22. ISSN 1134-2749.
- Parsons, Marie (2005). «Deir el-Medina» (en inglés). Consultado el 08, 10 de 2008.
Deir el-Medina
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Contenido
Deir el-Medina (Arabic: دير المدينة) is an ancient Egyptian village which was home to the artisans who worked on the tombs in the Valley of the Kings during the 18th to 20th dynasties of the New Kingdom period (ca. 1550-1080 BCE)[2] The settlement's ancient name was "Set Maat" (translated as "The Place of Truth"), and the workmen who lived there were called “Servants in the Place of Truth”.[3] During the Christian era the temple of Hathor was converted into a Church from which the Arabic name Deir el-Medina ( "the monastery of the town") is derived.[4]
At the time when the world's press was concentrating on Howard Carter's discovery of the Tomb of Tutankhamun in 1922 a team led by Bernard Bruyère began to excavate the site.[5] This work has resulted in one of the most thoroughly documented accounts of community life in the ancient world that spans almost four hundred years. There is no comparable site in which the organisation, social interactions, working and living conditions of a community can be studied in such detail.[6]
The site is located on the west bank of the Nile, across the river from modern-day Luxor.[7] The village is laid out in a small natural amphitheatre, within easy walking distance of the Valley of the Kings to the north, funerary temples to the east and south-east, with the Valley of the Queens to the west.[8] The village may have been built apart from the wider population in order to preserve secrecy in view of sensitive nature of the work carried out in the tombs.[9]
Contents[hide] |
[edit] Excavation history
A significant find of papyri was made in the 1840s in the vicinity of the village and many objects were also found during the course of the 19th century. The archaeological site was first seriously excavated by Ernesto Schiaparelli between 1905-1909 which uncovered large amounts of ostraca . A French team directed by Bernard Bruyère excavated the entire site, including village, dump and cemetery, between 1922-1951. Unfortunately through lack of control it is now thought that about half of the papyri recovered was removed without the knowledge or authorisation of the team director.[10] Around five thousand ostrica of assorted works of commerce and literature were found in a well close to the village.[11] Jaroslav Černý, who was part of Bruyère's team, went on to study the village for almost fifty years until his death in 1970 and was able to name and describe the lives of many of the inhabitants.[12] The peak overlooking the village was renamed "Mont Cernabru" in recognition of Černý and Bruyère's work on the village.[13]
[edit] The Village
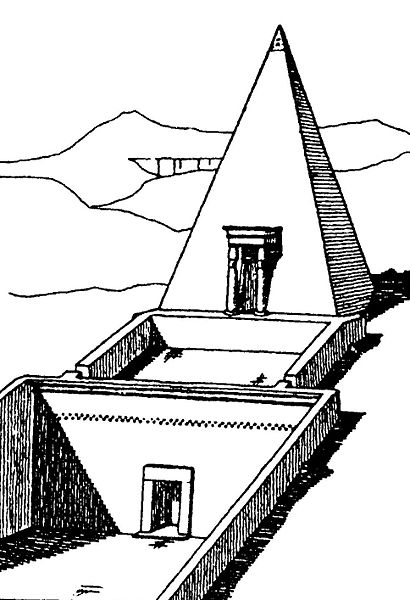
The first datable remains of the village belong to the reign of Thutmosis I (c. 1506-1493 BCE) with its final shape being formed during the Ramesside Period[14] At its peak the community contained around sixty-eight houses spread over at total area of 5,600 sq. m. with a narrow road running the length of the village.[15] The main road through the village may have been covered to shelter the villagers from the intense glare and heat of the sun.[5] The size of the habitations varied, with an average floor space of 70 sq. m., but the same construction methods were used throughout the village. Walls were made of mudbrick, built on top of stone foundations. Mud was applied to the walls which were then painted white on the external surfaces with some of the inner surfaces whitewashed up to a height of around one metre. A wooden front door might have carried the occupants name.[16] Houses consisted of four to five rooms comprising an entrance, main room, two smaller rooms, kitchen with cellar and staircase leading to the roof. The full glare of the sun was avoided by situating the windows high up on the walls.[2] The main room contained a mudbrick platform with steps which may have been used as a shrine or a birthing bed.[2] Nearly all houses contained niches for statues and small altars.[17] The tombs built by the community for their own use include small rock-cut chapels and substructures adorned with small pyramids.[18]
Due to its location, the village is not thought to have provided a pleasant environment: the walled village takes up the shape of the narrow valley in which its situated, with the barren surrounding hillsides reflecting the desert sun and the hill of Gurnet Murai cutting off the north breeze as well as the view of the verdant river valley.[19] The village was abandoned c. 1110-1080 BCE during the reign of Ramesses XI (whose tomb was the last of the royal tombs built in the The Valley of the Kings) due to increasing threats of Libyan raids and the instability of civil war.[20] The Ptolemies later built a temple to Hathor on the site of an ancient shrine dedicated to her.[21]
[edit] Historical texts of Deir el-Medina
The surviving texts record the events of daily life rather than major historical incidents.[22] Personal letters reveal much about the social relations and family life of the villagers. The ancient economy is documented by records of sales transactions that yield information on prices and exchange. Records of prayers and charms illustrate ordinary popular conceptions of the divine, whilst researchers into ancient law and practice find a rich source of information recorded in the texts from the village.[10] Many examples of the most famous works of Ancient Egyptian literature have also been found.[23] Thousands of papyri and ostraca still await publication.[24]
[edit] Village life
The settlement was home to a mixed population of Egyptians, Nubians and Asiatics who were employed as labourers, ( stone-cutters, plasterers, water-carriers), as well as those involved in the administration and decoration of the royal tombs and temples.[25] The artisans and the village were organised into two groups, left and right gangs who worked on opposite sides of the tomb walls similar to a ship's crew, with a foreman for each who supervised the village and its work.[2]
As the main well was thirty minutes walk from the village carriers worked to keep the village regularly supplied with water. When working on the tombs the artisans stayed overnight in a camp overlooking the mortuary temple of Queen Hatshepsut (c. 1479–1458 BCE) that is still visible today. Surviving records indicate that the workers had cooked meals delivered to them from the village.[5]
Based on analysis of income and prices, the workmen of the village would, in modern terms, be considered middle class. As salaried state employees they were paid in rations at up to three times the rate of a fieldhand, but unofficial second jobs were also widely practiced.[26] At great festivals such as the heb sed the workmen were issued with extra supplies of food and drink to allow a stylish celebration.[27]
The working week was eight days followed by two days holiday, though the six days off a month could be supplemented frequently due to illness, family reasons and, as recorded by the scribe of the tomb, rowing with wife or having a hangover.[28] Including the days given over to festivals, over one-third of the year was time-off for the villagers during the reign of Merneptah (c. 1213-1203 BCE).[29]
During their days off the workmen could work on their own tombs, and since they were amongst the best craftsmen in Ancient Egypt who excavated and decorated royal tombs, their own tombs are considered to be some of the most beautiful on the west bank.[28]
A large proportion of the community, including women, could at least read and possibly write.[30]
The jobs of the workers would have been considered desirable and prized positions with the posts being inheritable.[31]
The examples of love songs recovered show how friendship between the sexes was practised, as was social drinking by both men and women.[32] Egyptian marriages amongst commoners were monogamous but little is known about the marriage or wedding arrangements from surviving records.[33] It was not unusual for couples to have six or seven children with some recorded as having ten.[34]
Separation, divorce and remarriage occurred. Merymaat is recorded as wanting a divorce on account of his mother in-law's behaviour. Girl slaves could become surrogate mothers in cases were the wife was infertile and in doing so raise their status and procure their freedom[35]
The community could move freely in and out of the walled village but for security reasons only outsiders who had good work related reasons could enter the site.[5]
[edit] Women and village life
The records from this village provide most of the information we know about how women lived in the New Kingdom era.[36] Women were supplied with servants by the government to assist with the grinding of the grain and laundry tasks.[37] The wives of the workers cared for the children and baked the bread, a prime food source in these kind of societies. The vast majority of women who had a particular religious status embedded in their names were married to foremen or scribes and could hold the titles of chantress or singer with official positions within local shrines or temples, perhaps even within the major temples of Thebes.[36] Under Egyptian law they had property rights. They had title to their own wealth and a third of all marital goods. This would belong solely to the wife in case of divorce or death of the husband. If she died first it would go to her heirs, not to her spouse.[38][39] Brewing of beer was normally supervised by the Mistress of the House, though the workmen considered the monitoring of the activity as a legitimate excuse for taking time off work.[40]
[edit] Law and order
The workers and their families were not slaves but free citizens with recourse to the justice system as required. In principle any Egyptian could petition the vizier and could demand a trial by his peers.[41] The community had its own court of law made up of a foreman, deputies, craftsmen and a court scribe, and were authorised to deal with all civil and some criminal cases, typically relating to the non-payment of goods or services. The villagers represented themselves and cases could go on for several years, with one dispute involving the chief of police lasting eleven years.[28] The local police, Medjay, were responsible for preserving law and order as well as controlling access to the tombs in the Valley of the Kings.[28] One of the most famous cases recorded relates to Paneb the son of an overseer who was accused of looting royal tombs, adultery and causing unrest in the community. The outcome is not known but surviving records indicate the execution of a head of workmen at this time.[42]
The people of Deir el-Medina often consulted with oracles about many aspects of their lives including justice. Questions could be put in writing or orally before the image of the god when carried by priests upon a litter. A positive response could have been made by a downward dip and a negative by a withdrawal of the litter.[43] When a matter of justice came up and it wasn't resolved by a tribunal they would carry the statue to the accused and ask "Is it he who stole my goods" and if the statue nodded the accused would be considered guilty however at times the accused would deny guilt and demand to see another oracle or, in at least one case when that failed, he asked to see a third. When the third also nodded indicating guilt a judgement would be passed and he would have to make reparations and receive punishment. They also believed the oracle could punish or reward by bringing disease or blindness to people as punishment or miracle cures as rewards. [44]
[edit] Popular piety
See also Ancient Egyptian Religion
The excavations of the royal artisans community at Deir el-Medina have revealed much evidence of personal religious practice and cults.[43] State gods were worshipped freely alongside personal gods without any conflict between national and local modes of religious expression.[45]
The community had between sixteen-eighteen chapels, with the larger ones dedicated to Hathor , Ptah and Ramesses II. The workmen seem to have honoured Ptah and Reshep, the scribes Thoth and Seshat, as patron deities of their particular activity. Women had particular devotion towards Hathor, Taweret, and Bes in pregnancy, turning to Renenutet and Meretseger for food and safety.[46] Meretseger, "Lady of the Western Mountain", was perhaps, at a local level, at least as important as Osiris, the great god of the dead.[46]
The villagers held Amenhotep I (c. 1526-1506 BCE) and his mother Queen Ahmose Nefertari in high regard over many generations, possibly as divinized patrons of the community.[47] When Amenhotep died he became the centre of a village funerary cult, worshipped as "Amenhotep of the Town". When the Queen died she also was deified and became "Mistress of the Sky" and "Lady of the West".[48] Every year the villagers celebrated the Festival of Amenhotep I when the elders acted as priests in the ceremonies that paid honour to their own local gods who were not worshipped anywhere else in Egypt.[49]
Prayers were made and dedicated to a particular deity as votive offerings, similar in style to the penitential psalms in the Hebrew scriptures that express remorse and thanksgiving for mercy.[50] Stelae record sorrow for human error and humbly invoke a god for forgiveness and mercy. In one instance Meretseger is petitioned to bring relief to one in pain. She answer the prayer by bringing "sweet breezes".[51] On another stela a workman writes: "I was a man who swore falsely by Ptah, Lord of Truth, and he caused me to see darkness by day. Now I will declaim his might to both the ignorant and the knowledgeable.”[5] Amun was considered a special patron of the poor and one who was merciful to the penitent. A stelae records:
[Amun] who comes at the voice of the poor in distress, who gives breath to him who is wretched..You are Amun, the Lord of the silent, who comes at the voice of the poor, when I call to you in my distress You come and rescue me...Though the servant was disposed to do evil, the Lord is disposed to forgive. The Lord of Thebes spends not a whole day in anger, His wrath passes in a moment, none remains. His breath comes back to us in mercy..May your ka be kind, may you forgive, It shall not happen again.[52]
Dream interpretation, a gift which Hebrew scriptures also attribute to Joseph, was very common.[53] A book of dreams was found in Scribe Kenhirkhopeshef's library which was old even in his time. This book was used to interpret various types of dreams. These interpretations lacked precision and similar dreams often had different meanings. In many cases the interpretation was the opposite of what the dream depicted, for example a happy dream often signified sadness, a dream of plenty often signified scarceness etc.
Examples of how the dreams are interpreted include the following:
- If a man sees himself dead this is good; it means a long life in front of him.
- If a man sees himself eating crocodile flesh this is good; it means acting as an official amongst his people. (i.e. becoming a tax collector)
- If a man sees himself with his face in a mirror this is bad; it means a new life.
- If a man sees himself uncovering his own backside this is bad it means he will be an orphan later. [54]
[edit] Strike
The royal building service was usually well run in view of the importance of the work it carried out. Paying proper wages was a religious duty that formed an intrinsic part of Maat. When this broke down it indicated problems in the wider state.[55] The coming of the iron age and collapse of empire led to economic instability with inflation a notable feature. The high ideals expressed in the code of Maat became strained and this provided the background to workers unrest.[56]
In about the 25th year the reign of Ramses III (c. 1170 BCE) the laborers were so exasperated by delays in supplies they threw down their tools and walked off the job in what may have been the first sit down strike in history. They wrote a letter to the Vizier complaining about lack of wheat rations. Village leaders attempted to reason with them but they refused to return to work until their grievances were addressed. They responded to the elders with "great oaths". "we are hungry", the crews claimed; "eighteen days have passed this month" and they still had not received their rations. They were forced to buy their own wheat. They told them to send to Pharaoh or vizier to address their concerns. After the authorities heard of their complaints they addressed them and they went back to work the next day. There were several strikes that followed after one of them when the strike leader asked the workers to follow him they told them they had enough and returned to work. This was not the last strike but they soon restored the regular wheat supplies and the strikes came to an end for the remaining years of Ramesses III. However since the chiefs supported the authorities the workers no longer trusted them and chose their own representatives. [57] Further complaints by the artisans are recorded forty and fifty years after the initial dispute, during the reigns of Ramesses IX and Ramesses X.[58]
[edit] Tomb Robbing
After the reign of Ramses IV (c. 1155-1149 BCE) the conditions of the village became increasingly unsettled. At times there was no work for fear of the enemy. The grain supplies became less dependable and this was followed by more strikes. Gangs of tomb robbers increased often tunnelling in through the back so they wouldn't break the seal and be exposed. A tomb robbing culture developed that included fences and even some officials who accepted bribes. When the Vizier checked the tombs if the seals were undisturbed they wouldn't report it as being opened. When they finally did catch tomb robbers they used limb twisting tactics to interrogate the tomb robbers and obtain information about where the plunder was and who their accomplices were. On one occasion when some officials were looking for a scapegoat they obtained a confession from a repeat offender after torturing him. However the Vizier was suspicious at how easy he was produced and asked him to lead them to the tomb he robbed. He led them to an unfinished tomb that was never used and claimed it was the tomb of Isis.
When they retrieved the plunder they didn't return it to the tombs; instead they added it to the treasury. [59][60]
[edit] See also
[edit] Bibliography
- Jaroslav Černý, "A Community of Workmen at Thebes in the Ramesside Period", Kairo 1973.
- Leonard H. Lesko, ed (1994). Pharaoh's Workers: The Villagers of Deir El Medina. Cornell University Press. ISBN 0-8014-8143-0.
- Wilson, Hilary (1997). Peoples of the Pharaohs: From Peasant to Courtier. Brockhampton Press. ISBN 1-86019-900-3.
- Romer, John. Ancient Lives Daily Life in Egypt of the Pharaohs.
- Time Life Lost Civilizations series: Egypt: Land of the Pharaohs. 1992.
- Tyldesley, Joyce (1996). Hatchespsut: The Female Pharaoh. Viking. ISBN 0-670-85976-1.
- A.G McDowell, “Village Life in Ancient Egypt: Laundry Lists and Love Songs”, Oxford University Press, 2002, ISBN 0199247536
- M. L. Bierbrier, "The Tomb-builders of the Pharaohs”, American University in Cairo Press, p125, 1989, ISBN 9774242106
- Edited I.E.S Edwards – C.J Gadd – N.G.L Hammond- E.Sollberger, “The Cambridge Ancient History: II Part I , The Middle East and the Aegean Region, c.1800-13380 B.C”, Cambridge at the University Press, 1973, ISBN 0-521-08230-7
- Lorna Oaks, “The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Pyramids Temples & Tombs of Ancient Egypt", Peviously Published as “Sacred Sites of Ancient Egypt”, Southwater, 2006, ISBN 978-1-84476-279-8
- Lynn Meskell, "Private life in New Kingdom Egypt", Princeton University Press, 2002, ISBN 069100448X
[edit] External links
 Media related to Deir el-Medina at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Deir el-Medina at Wikimedia Commons- YouTube video clip of Deir -el-Medina 1.
- YouTube video clip of Deir -el-Medina 2.
- Photographs of Deir el-Medina
- A Survey of the New Kingdom Non-literary Texts from Deir el-Medina - Leiden University (Database)
| |||
| |||
Coordinates: 25°43′44″N 32°36′05″E / 25.72889°N 32.60139°E
[edit] References
- ^ "Archaeologica: the world's most significant sites and cultural treasures", Aedeen Cremin, p384, frances lincoln, 2007, ISBN 0711228221
- ^ a b c d Oakes, p110
- ^ Lesko, p.7
- ^ Bierbrier, p125
- ^ a b c d e "Pharaoh’s Workers: How the Israelites Lived in Egypt", Leonard and Barbara Lesko, Biblical Archaeological Review, Jan/Feb 1999
- ^ Cambridge Ancient History, p380
- ^ Lesko p.2
- ^ Cambridge Ancient History, p379
- ^ "Archaeologica: the world's most significant sites and cultural treasures", Aedeen Cremin, p91, Frances Lincoln, 2007, ISBN 0711228221
- ^ a b Lesko, p8
- ^ "Archaeologica: the world's most significant sites and cultural treasures", Aedeen Cremin, p91, Frances Lincoln, 2007, ISBN 0711228221
- ^ "Life of the ancient Egyptians, Eugen Strouhal, Evžen Strouhal, Werner Forman, Editorial Galaxia, p187, 1992, ISBN 080612475XIn
- ^ Romer, p. 209
- ^ McDowell p18, p21
- ^ McDowell p9
- ^ McDowell p11, p12
- ^ Paul Johnson, "The Civilization of Ancient Egypt", p131, Book Club Associates (org pub by Weidenfield & Nicolson), 1978
- ^ Donald B. Redford (Editor), "Oxford Guide to Egyptian Mythology", p378, Berkley Reference, 2003, ISBN 0-425-19096-X
- ^ Lesko, p.2
- ^ Bierbrier p119&120
- ^ McDowell p4
- ^ Lesko, p2
- ^ Lesko p132,133
- ^ McDowell p8
- ^ Cambridge Ancient History, p379-380
- ^ Lesko, p12
- ^ Wilson (1997), p118 & p222
- ^ a b c d Oakes, p111
- ^ Romer, p. 48
- ^ Wilson (1997), p.72
- ^ Lesko, p22
- ^ Lesko p34
- ^ Lesko p35
- ^ Meskell, p74
- ^ Meskell, p95-98
- ^ a b Lesko p28
- ^ Lesko p36
- ^ Time Life (1992) p.134-142
- ^ Romer
- ^ Wilson (1997) p69
- ^ Lesko p38
- ^ "Archaeologica: the world's most significant sites and cultural treasures", Aedeen Cremin, p91, Frances Lincoln, 2007, ISBN 0711228221
- ^ a b Donald B. Redford (Editor), "Oxford Guide to Egyptian Mythology", p80, Berkley Reference, 2003, ISBN 0-425-19096-X
- ^ Romer, p.100-115,178
- ^ "Religion and Magic in Ancient Egypt", Rosalie David, p277, Penguin, 2002, ISBN 0-14-026252-0
- ^ a b Lesko p90
- ^ Lesko, p7,111
- ^ Tyldesley (1996), p62
- ^ Wilson, p118
- ^ Donald B. Redford (Editor), "Oxford Guide to Egyptian Mythology", p313, Berkley Reference, 2003, ISBN 0-425-19096-X
- ^ "Egyptian Myths", George Hart, p46, University of Texas Press, 1990, ISBN 0292720769
- ^ "Ancient Egyptian Literature", Miriam Lichtheim, p105-106, University of California Press, 1976, ISBN 0-520-03615-8
- ^ John Romer, "Testament", p50, Guild Publishing,1988
- ^ Romer, p.68-72
- ^ Paul Johnson, "The Civilization of Ancient Egypt", p110, Book Club Associates (org pub by Weidenfield & Nicolson), 1978
- ^ "The Burden of Egypt", John A. Wilson, p278-279, University of Chicago Press, 1951, 4th imp 1963
- ^ Romer, p.116-125
- ^ "The Burden of Egypt", John A. Wilson, p278, University of Chicago Press, 1951, 4th imp 1963
- ^ Romer, p.145-210
- ^ Time Life (1992) p. 134-142
related articles
- Servant in the Place of Truth
- Theban Necropolis
- TT7
- TT3
- TT5
- TT2
- TT4
- Valley of the Kings
- TT1
- Valley of the Queens